How to File Salary Schedule in ITR: Step-by-Step Guide for Indian Taxpayers
Learn how to file Schedule Salary in your Indian Income Tax Return (ITR) with this step-by-step guide. Avoid common mistakes, understand deductions, and ensure accurate filing for a hassle-free tax experience.

Filing your Income Tax Return (ITR) can seem like a daunting task, especially if you're doing it for the first time or have income from multiple sources. However, understanding the process, particularly the section dealing with your salary income (Schedule Salary), can simplify the filing process considerably. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step, ensuring you accurately report your salary income and claim eligible deductions.
Understanding Schedule Salary
Understanding Schedule Salary: Your Key to Reporting Salary Income
Schedule Salary is the designated section within your Income Tax Return (ITR) form where you disclose your entire income earned through salary or pension. It encompasses various components that contribute to your overall remuneration:
1. Basic Salary: This forms the fundamental part of your salary, representing the fixed compensation you receive for your services. It is typically the largest component of your salary package.
2. Allowances: These are supplementary payments provided by your employer to cover specific expenses or needs. Common allowances include:
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): Aids in covering your accommodation expenses. It can be partially or fully exempt from tax based on certain conditions.
- Dearness Allowance (DA): Designed to offset the impact of inflation on your purchasing power.
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA): Facilitates travel expenses for you and your family.
- Other Allowances: May include medical allowances, conveyance allowances, etc., depending on your employer's policies.
3. Perquisites: These are non-cash benefits extended by your employer, often referred to as "perks." Examples include:
- Rent-free Accommodation: If your employer provides housing, its value is considered a perquisite.
- Company Car: The value of using a company-provided car for personal purposes is a taxable perquisite.
- Other Perks: May include free meals, club memberships, medical facilities, etc.
4. Profit in lieu of Salary: This is a special type of compensation you receive when you choose to forgo a salary increment, bonus, or other benefits.
5. Retirement Benefits: This category covers income received after your retirement, such as pension, gratuity, or other post-retirement benefits.
Your Arsenal for Filing Schedule Salary: Essential Documents
Gathering and organizing the following documents before you begin filling Schedule Salary will streamline the process and ensure accuracy:
1. Form 16: Your Salary Bible
- This is the cornerstone document for salaried individuals. Issued by your employer annually, it serves as a comprehensive summary of your salary, allowances, perquisites, and tax deductions (TDS) made throughout the financial year.
- It contains crucial information like your PAN, employer's TAN, gross salary, various allowances, TDS amount, and details of deductions claimed under Chapter VI-A of the Income Tax Act.
- Form 16 is typically divided into Part A (containing TDS details) and Part B (providing a detailed salary breakup).
2. Salary Slips: Monthly Insights
- Your monthly salary slips provide a detailed breakdown of your salary components for each month of the financial year.
- They reveal your basic salary, HRA, DA, other allowances, deductions like provident fund (PF) and professional tax, and the net salary credited to your bank account.
- Cross-referencing your salary slips with Form 16 helps verify the accuracy of the information and identify any discrepancies.
3. Form 26AS: Your Tax Mirror
- Form 26AS is your annual tax statement, reflecting all taxes deposited against your PAN by various deductors, including your employer.
- It acts as a consolidated record of TDS, advance tax payments, self-assessment tax, and any refunds received.
- It's crucial to reconcile the TDS details mentioned in your Form 16 with those in Form 26AS to ensure they match and avoid any discrepancies that could lead to notices from the tax department.
- You can easily access Form 26AS through the Income Tax Department's e-filing portal.
4. Proof of Investments: Claiming Your Due
- If you have made investments eligible for tax deductions under various sections of the Income Tax Act, such as:
- Section 80C: Investments in ELSS mutual funds, PPF, life insurance premiums, etc.
- Section 80D: Health insurance premiums for self, family, and parents.
- Section 80E: Interest paid on education loan.
- You'll need to furnish the relevant documents as proof of these investments. These may include:
- Insurance premium receipts
- Mutual fund statements
- Home loan statements
- Tuition fee receipts (for education loan)
- Having these documents readily available will facilitate a smooth claiming process for deductions and help you maximize your tax savings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Filing Schedule Salary in ITR
1. Access the ITR Utility:

- Online: The easiest way is to use the online ITR filing utility on the Income Tax Department's e-filing portal:
https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal/ - Offline: You can download the offline utility or use third-party tax filing software.
2. Choose the Correct ITR Form:
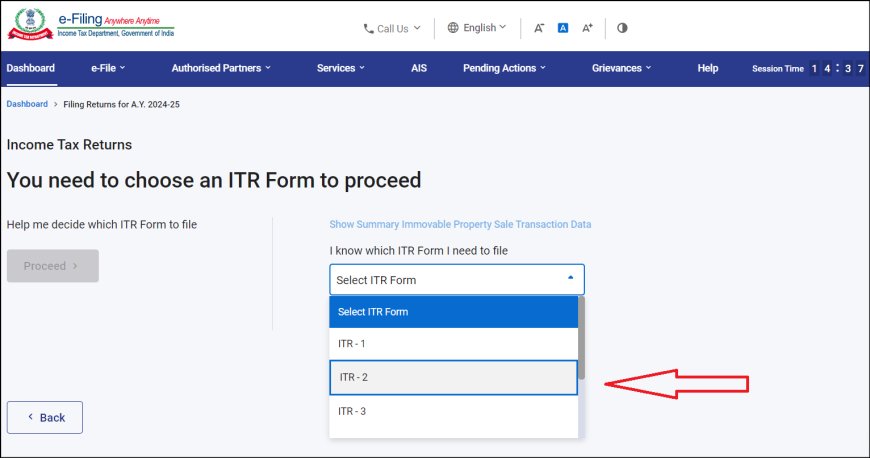
- ITR-1 (Sahaj): If your income is solely from salary, one house property (self-occupied or let out), and other sources (interest, etc.) up to ₹50 lakhs.
- ITR-2: If your income exceeds ₹50 lakhs, you have capital gains, or income from more than one house property.
- Other ITR forms: Depending on your specific income sources and residential status (ITR-3, ITR-4, etc.).
3. Navigate to Schedule Salary:
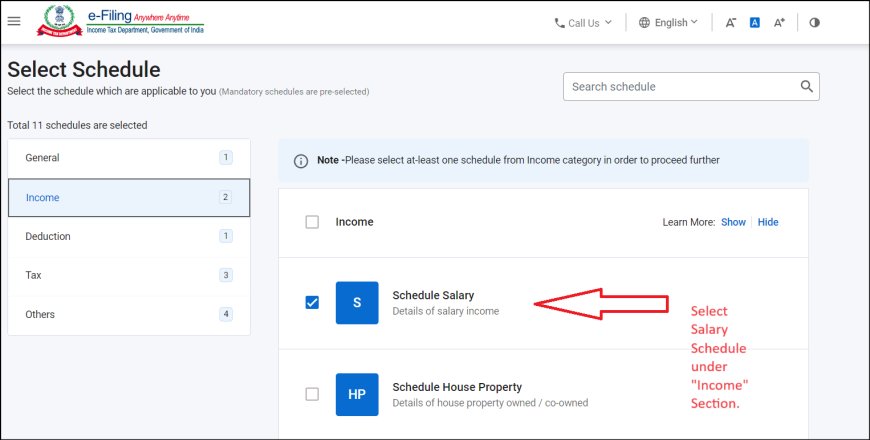
- In the ITR utility, look for the section called "Income Details" or "Gross Total Income."
- Under this, you'll find "Income from Salary/Pension." Click on it to open Schedule Salary.
4. Fill in the Details:
- Employer Details: Enter your employer's name, Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN), and address.
- Income Details: Refer to your Form 16 (provided by your employer) and salary slips. Carefully fill in the following:
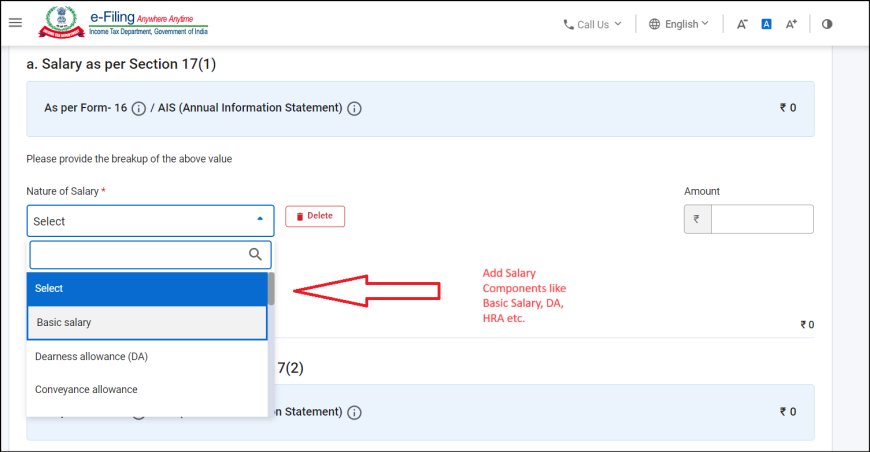
-
- Gross Salary: Basic salary + Dearness Allowance (DA) + House Rent Allowance (HRA) + other allowances + perquisites + profit in lieu of salary.
- Allowances not Exempt: This might include the portion of your HRA that is taxable.
- Value of Perquisites: This includes the value of benefits like a company car, accommodation, etc. [Section 17(2)]
- Profit in lieu of Salary: If applicable. [Section 17(3)]
- Deductions under Section 16:
- Standard deduction (currently ₹50,000).
- Entertainment allowance (if applicable, for government employees).
- Professional tax.
- Income Chargeable under the Head "Salaries": This is automatically calculated based on the above information.
5. Verify with Form 26AS:
- Form 26AS is your tax credit statement. Cross-check the details of the Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) from your salary, as mentioned in Form 16, with the details in Form 26AS. Ensure they match to avoid discrepancies.
6. Claim Deductions (Optional):

- If eligible, claim deductions under various sections of the Income Tax Act, such as:
- Section 80C: For investments like PPF, ELSS, life insurance premiums, etc. (up to ₹1.5 lakhs limit).
- Section 80D: For health insurance premiums.
- Section 80E: For interest on education loans.
7. Review and Submit:
- Double-check all the information you've entered in Schedule Salary and the entire ITR.
- Once satisfied, submit your ITR. You'll receive an acknowledgment number for your records.
Schedule Salary Simplified: A Practical Example for Beginners
1. Choosing the Right ITR Form:
- Priya's income is only from her salary, and it's below ₹50 lakhs. So, she can file ITR-1 (Sahaj).
2. Accessing the ITR Utility:
- Priya logs into the Income Tax e-filing portal and starts filling out her ITR-1 form online.
3. Navigating to Schedule Salary:
- Priya finds the "Income Details" section and clicks on "Income from Salary/Pension," which opens Schedule Salary.
4. Filling in the Details:
- Employer Details: Priya enters her employer's name as "XYZ Tech Solutions," the TAN as "DELA12345F," and the address as per her Form 16.
- Income Details: From her Form 16, Priya fills in the following:
- Gross Salary: ₹8,00,000
- Allowances not Exempt: ₹20,000 (This could be the taxable portion of her HRA)
- Value of Perquisites: ₹30,000 (This could be the value of benefits like a company car)
- Profit in lieu of Salary: ₹0 (Priya didn't receive any)
- Deductions under Section 16:
- Standard Deduction: ₹50,000
- Entertainment Allowance: ₹0 (Not applicable to her)
- Professional Tax: ₹2,400
- Income Chargeable under "Salaries": This is automatically calculated by the utility based on the above information.
5. Verify with Form 26AS:
- Priya logs into her e-filing account and views her Form 26AS. She verifies that the TDS amount mentioned in Form 16 matches the TDS credit shown in Form 26AS.
6. Claiming Deductions (Optional):
- Priya invests ₹1,20,000 in ELSS mutual funds. She claims this deduction under Section 80C.
7. Review and Submit:
- Priya carefully reviews all the details she has entered in Schedule Salary and the rest of her ITR. After confirming everything, she submits her ITR.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing Schedule Salary
1. Incorrect Employer Details:
- Mistake: Entering the wrong TAN (Tax Deduction and Account Number), employer name, or address.
- How to Avoid: Double-check these details against your Form 16. A single incorrect digit in the TAN can cause problems.
2. Mismatching TDS Details:
- Mistake: The TDS deducted from your salary as shown in Form 16 doesn't match the TDS credited in your Form 26AS (tax credit statement).
- How to Avoid: Carefully compare both forms. If there's a mismatch, contact your employer to rectify the error.
3. Not Claiming Eligible Deductions:
- Mistake: Failing to claim deductions under Section 80C, 80D, or other applicable sections. This can lead to paying more taxes than necessary.
- How to Avoid: Thoroughly review the list of available deductions. Gather the necessary documents (investment proofs, medical bills, etc.) to support your claims.
4. Ignoring Exempt Allowances:
- Mistake: Not claiming the exemption on allowances like HRA (House Rent Allowance) or LTA (Leave Travel Allowance) when eligible.
- How to Avoid: Understand the rules for exempt allowances. For example, HRA exemption depends on factors like the rent paid, city of residence, and your salary structure.
5. Incorrect Calculation of Taxable Income:
- Mistake: Adding all allowances and perquisites to your salary without considering the exemptions and deductions.
- How to Avoid: Carefully calculate your taxable income as per the Income Tax rules. You can use online tax calculators or consult a tax professional if needed.
6. Not Reporting Salary from Previous Employers:
- Mistake: If you changed jobs during the financial year, not reporting salary received from the previous employer.
- How to Avoid: Collect Form 16 from all employers and include the income from each in your ITR.
7. Not Verifying ITR-V:
- Mistake: Forgetting to e-verify or send the signed ITR-V (acknowledgment) within the specified time, making your ITR invalid.
- How to Avoid: E-verify your ITR online through Aadhaar OTP, net banking, etc., or send the signed ITR-V to the Centralized Processing Centre (CPC) within 120 days of filing.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of filing Schedule Salary in your ITR is a crucial step towards fulfilling your tax obligations accurately and efficiently. While it may seem intricate at first, armed with the right information, resources, and a meticulous approach, you can navigate through the process with confidence. Remember, every detail counts, from verifying employer information to claiming eligible deductions. By avoiding common pitfalls and double-checking your entries, you ensure a smooth filing experience, ultimately contributing to a transparent and compliant tax ecosystem. If uncertainties arise, seeking guidance from tax professionals can be invaluable. As tax laws evolve, staying informed and adapting your approach will empower you to file your returns accurately year after year, paving the way for a financially sound future.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as professional tax or legal advice. Tax laws and regulations can be complex and are subject to change. We strongly recommend consulting with a qualified tax advisor or chartered accountant for personalized advice regarding your specific financial situation and tax obligations. The authors and publishers of this article do not assume any responsibility for errors, omissions, or any losses that may arise from reliance on the information presented herein.
What's Your Reaction?
































































































































