ITR-2 Filing Guide (AY 2024-25): A Step-by-Step Guide for Indian Taxpayers
This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of filing ITR-2 for Assessment Year 2024-25, covering eligibility, required documents, online filing instructions, common mistakes to avoid, and the benefits of timely filing. Simplify your tax return process and ensure compliance with Indian tax laws.

Filing your income tax return (ITR) can seem like a daunting task, especially if you're unfamiliar with the process or have complex income sources. However, with a little guidance and preparation, it can be quite straightforward. In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through every step of filing ITR-2 for Assessment Year (AY) 2024-25, ensuring a smooth and stress-free experience.
What is ITR-2?
ITR-2 is a form used by individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) who have income from sources other than profits and gains from business or profession. If you've earned income from salary, house property, capital gains, or other sources like interest or dividends, and you don't qualify for ITR-1, then ITR-2 is the form for you.
Who Should File ITR-2?
You should file ITR-2 if you fall under any of the following categories:
1. Individuals and HUFs who have income from sources other than a business or profession:
- Salary/Pension: If you receive income from a job or pension.
- House Property: If you own and earn rental income from house property (more than one house property).
- Capital Gains: If you've made profits or losses from selling assets like stocks, mutual funds, or property.
- Other Sources: If you have income from sources like interest on savings accounts or fixed deposits, dividends, or winnings from lotteries.
2. Individuals with income from capital gains (including sale of property or investments):
- Short-term Capital Gains: Profits from selling assets held for less than a specified period (usually 36 months).
- Long-term Capital Gains: Profits from selling assets held for a longer duration.
3. Individuals with foreign income or assets:
- Foreign Income: If you earn income from sources outside India, like a job in another country or rental income from a property abroad.
- Foreign Assets: If you own assets located outside India, such as bank accounts, real estate, or investments.
4. Individuals with agricultural income exceeding ₹5,000:
- Agricultural Income: Income earned from agricultural activities like farming or growing crops.
Who Cannot File ITR-2?
While ITR-2 is suitable for a wide range of taxpayers, certain individuals are not eligible to use this form for filing their income tax returns:
1. Individuals or HUFs with income from Business or Profession:
- Business Income: If you earn income from running a business, such as a sole proprietorship or partnership firm, you cannot file ITR-2.
- Professional Income: Similarly, if your income is derived from a profession like medicine, law, engineering, or accounting, you are ineligible for ITR-2.
2. Individuals Eligible to File ITR-1 (Sahaj):
- Simplified Form: ITR-1 is a simpler form designed for individuals with specific income sources and a total income not exceeding ₹50 lakhs. If you meet the criteria for ITR-1, you are not allowed to file ITR-2.
3. Individuals Who are a Director in a Company and Have Held Unlisted Equity Shares at Any Time During the Year:
- Director's Income: If you receive remuneration as a director in a company and own unlisted equity shares, you cannot file ITR-2.
4. Individuals Opting for the Presumptive Taxation Scheme:
- Presumptive Taxation: This scheme simplifies tax calculations for certain businesses and professions. If you opt for this scheme, you cannot file ITR-2.
5. Individuals with Income from a Partnership Firm:
- Partnership Income: If you are a partner in a firm and receive income from the partnership, you cannot file ITR-2.
Documents Required for Filing ITR-2 (AY 2024-25)
Before you start the process of filing your ITR-2, it's crucial to gather all the necessary documents. Having these documents organized will ensure a smooth and efficient filing experience. Here's an expanded list of the essential documents you'll need:
1. PAN Card:
- Purpose: Your Permanent Account Number (PAN) is a unique 10-digit alphanumeric identifier issued by the Income Tax Department. It's a mandatory requirement for filing your income tax return.
2. Aadhaar Card:
- Purpose: The government mandates linking your Aadhaar (12-digit unique identification number) with your PAN. This linkage is essential for verifying your identity and preventing tax fraud.
3. Form 16:
- Purpose: This form is issued by your employer and serves as a salary certificate. It provides details of your salary income, allowances, deductions, and tax deducted at source (TDS) throughout the financial year.
4. Form 26AS:
- Purpose: Your Form 26AS is an annual consolidated tax statement. It shows details of all taxes deducted on your behalf, including TDS on salary, interest income, and other sources. It also reflects any self-assessment or advance tax payments you've made.
5. Bank Statements/Passbooks:
- Purpose: These documents are needed to verify the interest income you've earned on your savings accounts, fixed deposits (FDs), and recurring deposits (RDs).
6. Investment Proofs:
- Purpose: Gather all documents related to your investments. This includes statements for mutual funds, stocks, bonds, equity-linked saving schemes (ELSS), and any other investment instruments you hold. You may need to report capital gains or losses from these investments.
7. Home Loan Documents:
- Purpose: If you have a home loan, you'll need documents like your home loan statement, provisional interest certificate, and principal repayment certificate. These documents help you claim deductions on the interest paid on your home loan.
8. Capital Gains Statements:
- Purpose: If you've sold any capital assets like property, stocks, or mutual funds during the financial year, you'll need statements showing the sale price, purchase price, and the resulting capital gains or losses.
9. Other Income Proofs:
- Purpose: Collect any documents related to other income sources you may have. This could include rental income receipts, income from freelancing or consulting, or any other miscellaneous income.
Additional Documents (If Applicable):
- Form 16A/16B/16C: If you've received income from sources other than salary and TDS has been deducted, you'll need these TDS certificates.
- Form 10E: If you're claiming relief under section 89 for salary arrears received, you'll need this form.
- Proof of Donations: If you've made any charitable donations eligible for tax deductions, keep the receipts handy.
Understanding the ITR-2 Form
The ITR-2 form is a comprehensive document designed to capture details of your income from various sources and the applicable deductions. Let's break down the key sections and schedules within the form:
Part A: General Information
The "Part A: General Information" section of the ITR-2 form is where you provide essential details about yourself or your Hindu Undivided Family (HUF). This section lays the foundation for your income tax return and is crucial for accurate processing. Here's an expanded look at the information you need to provide:
1. Personal Information:
- PAN: Enter your Permanent Account Number (PAN), a 10-digit alphanumeric identifier issued by the Income Tax Department. It's a mandatory field for all taxpayers.
- Aadhaar Number: Provide your 12-digit Aadhaar number. Linking your Aadhaar with your PAN is compulsory for filing your return.
- Name: Enter your full name as per your PAN card.
- Date of Birth: Provide your date of birth in DD/MM/YYYY format.
2. Filing Status:
- Individual: Select this option if you are filing the return as an individual taxpayer.
- HUF: Choose this if you are filing on behalf of a Hindu Undivided Family.
3. Address:
- Residential Status: Indicate whether you are a resident, non-resident, or resident but not ordinarily resident in India.
- Address Details: Provide your complete residential address, including flat/door/block number, name of premises/building/village, road/street/post office, area/locality, town/city/district, state, and PIN code.
4. Email ID and Mobile Number:
- Email ID: Enter your valid email address. This is essential for receiving communication from the Income Tax Department.
- Mobile Number: Provide your mobile number. You might receive OTPs (One-Time Passwords) for verification purposes.
5. Nature of Employment:
- Government: Select this if you are employed by the central or state government.
- PSU (Public Sector Undertaking): Choose this if you work for a government-owned enterprise.
- Pensioner: Indicate this if you are receiving a pension.
- Others: Select this option for any other type of employment (e.g., private sector).
6. Bank Account Details:
- Bank Name: Provide the name of your bank.
- Account Number: Enter your bank account number where you want to receive any tax refunds.
- IFSC Code: This is the Indian Financial System Code, a unique 11-digit code for identifying your bank branch.
- Account Type: Specify whether it's a savings or current account.
7. Additional Information (If Applicable):
- Filing Section: If you are filing the return under a specific section of the Income Tax Act (e.g., Section 139(1)), mention it here.
- Return Filed in Response to Notice: If you're filing in response to a notice from the Income Tax Department, indicate so.
- Revised Return: If you're filing a revised return to correct any errors in a previously filed return, select this option.
Part B: Total Income (TI)
Part B of the ITR-2 form is where you comprehensively report your total income from various sources. It comprises multiple schedules, each dedicated to a specific income type. Let's delve deeper into each of these schedules:
1. Schedule S: Income from Salaries
- Purpose: This schedule is exclusively for reporting income earned from your employment.
- Details:
- Basic Salary: Your regular salary component.
- Allowances: Includes house rent allowance (HRA), dearness allowance (DA), leave travel allowance (LTA), and other allowances.
- Perquisites: Non-cash benefits like company car, accommodation, etc.
- Profit in lieu of Salary: Compensation received in lieu of salary.
- Deductions: Includes standard deduction, entertainment allowance, and professional tax.
2. Schedule HP: Income from House Property
- Purpose: This schedule is for reporting income and expenses related to house property.
- Details:
- Rental income: Rent received from your property/properties.
- Municipal taxes: Property taxes paid.
- Interest on home loan: Interest component of your home loan EMIs.
- Standard deduction: 30% of the net annual value (NAV) as a standard deduction for property maintenance.
- Other deductions: Certain deductions like interest on borrowed capital for renovation or construction.
3. Schedule CG: Capital Gains
- Purpose: This schedule deals with gains and losses arising from the sale of capital assets.
- Details:
- Short-term Capital Gains (STCG): Gains from assets held for 36 months or less (12 months for equity shares/units of equity-oriented funds).
- Long-term Capital Gains (LTCG): Gains from assets held for more than 36 months (more than 12 months for equity shares/units of equity-oriented funds).
4. Schedule 112A & Schedule 115AD(1)(iii) proviso:
- Purpose: To report long-term capital gains on the sale of equity shares or units of equity-oriented funds/business trusts on which Security Transaction Tax (STT) is paid, for resident and non-resident taxpayers, respectively.
5. Schedule VDA:
- Purpose: To report income from the transfer of Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) like cryptocurrencies.
6. Schedule OS: Income from Other Sources
- Purpose: This is a catch-all schedule for reporting income from sources not covered elsewhere.
- Details:
- Interest income from savings accounts, FDs, RDs, etc.
- Dividend income.
- Family pension.
- Agricultural income exceeding ₹5,000.
- Winnings from lotteries, crossword puzzles, horse races, etc.
- Any other miscellaneous income.
7. Schedule SPI, SI, EI, PTI:
- Purpose: These schedules pertain to income of specified persons (SPI), income taxable at special rates (SI), exempt income (EI), and pass through income details from business trust or investment fund (PTI), respectively.
8. Schedule CYLA, BFLA, CFL:
- Purpose: These schedules are for reporting and adjusting losses.
- CYLA: Losses incurred in the current year.
- BFLA: Unabsorbed losses brought forward from previous years.
- CFL: Losses carried forward to future years.
Part C: Deductions and Total Taxable Income (TTI)
Part C of the ITR-2 form is where you claim deductions to reduce your total taxable income (TTI). This is a crucial step as it can significantly lower your tax liability. Let's delve deeper into Schedule VI-A, which lists the various deductions you can claim:
Schedule VI-A: Deductions Under Chapter VI-A
This schedule encompasses a wide range of deductions available to taxpayers under Chapter VI-A of the Income Tax Act. Some of the most common deductions include:
1. Section 80C:
- Purpose: This is one of the most popular deductions, offering a maximum limit of ₹1.5 lakhs for various investments and expenses.
- Eligible Investments/Expenses:
- Life insurance premiums
- Equity Linked Saving Schemes (ELSS)
- Public Provident Fund (PPF)
- National Savings Certificates (NSC)
- Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
- Principal repayment of home loan
- Tuition fees for children's education (up to two children)
- Certain pension schemes, etc.
2. Section 80D:
- Purpose: This deduction is for medical insurance premiums paid for yourself, your spouse, dependent children, and parents.
- Eligible Expenses:
- Health insurance premiums
- Preventive health check-up expenses
- Medical expenses for senior citizens (with or without insurance)
3. Section 80G:
- Purpose: This deduction is for donations made to specific charitable organizations.
- Eligible Donations:
- Donations to the Prime Minister's National Relief Fund
- Donations to the National Defence Fund
- Donations to specific charitable institutions approved by the government
4. Other Important Deductions:
- Section 80E: Interest paid on education loan
- Section 80EE: Additional interest on home loan
- Section 80EEA: Interest on affordable housing loan
- Section 80DDB: Medical treatment of specified diseases
- Section 80U: Deduction for individuals with disabilities
Part D: Computation of Tax Payable
Part D of the ITR-2 form is where your final tax liability is determined. This part takes into account your total income, deductions, taxes paid in advance, and taxes deducted at source (TDS) to calculate the exact amount of tax you owe or the refund you may be eligible for. Let's explore the key components of Part D:
1. Schedule Part B-TI:
- Purpose: This schedule summarizes your total income (TI) from all the different sources reported in Part B.
- Components:
- Total of all incomes from Schedule S (Salary), HP (House Property), CG (Capital Gains), OS (Other Sources), 112A, 115AD(1)(iii) proviso, VDA, SPI, SI, PTI, and Schedule BFLA.
- Gross Total Income (GTI) is calculated by adding all these income figures.
2. Schedule Part B-TTI:
- Purpose: This schedule calculates your Total Taxable Income (TTI) after deducting allowable exemptions and deductions.
- Components:
- Gross Total Income (GTI) is brought forward from Schedule Part B-TI.
- Deductions under Chapter VI-A are subtracted from GTI.
- Total Taxable Income (TTI) is the final figure after subtracting deductions.
3. Schedule IT:
- Purpose: This schedule calculates your tax liability based on the applicable income tax slab rates.
- Components:
- Total Taxable Income (TTI) is considered.
- Tax rates for the relevant assessment year are applied to calculate the tax payable.
- Rebate under section 87A is calculated and deducted (if eligible).
- Surcharge (if applicable) and Health and Education Cess are added.
4. Schedule TDS:
- Purpose: This schedule details the Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) from your various income sources.
- Components:
- TDS on Salary (as per Form 16)
- TDS on income other than salary (as per Form 16A, 16B, 16C)
- Details of TCS (Tax Collected at Source)
5. Schedule TCS:
- Purpose: This schedule is for reporting Tax Collected at Source (TCS) on sale of specified goods like liquor, timber, scrap, etc., above a certain threshold.
6. Schedule ESOP:
- Purpose: If you have income from Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOPs), you need to report it here.
Final Calculation of Tax Payable:
- Tax Payable is calculated by subtracting TDS, TCS, advance tax, and any other tax credits from the total tax liability.
- If the tax payable is negative, it indicates a refund due to you. If it's positive, you need to pay the remaining amount.
Key Points:
- Accuracy: Ensure that all TDS/TCS details are correctly entered as per your Form 16/16A/26AS.
- Double-Check: Verify all calculations to ensure accurate tax computation.
- Payment: If you have any tax due, pay it online through the e-filing portal before submitting your return.
Other Schedules and Verification in ITR-2 Form
While the main parts of ITR-2 cover your income, deductions, and tax computation, there are additional schedules that cater to specific situations and the final verification process.
Schedule FA: Foreign Assets and Income
- Purpose: This schedule is mandatory if you have any foreign assets or income during the financial year.
- Details:
- Details of foreign bank accounts held, along with their balances.
- Details of foreign properties or investments owned.
- Income earned from foreign sources, like salary, rental income, or capital gains.
- If you are a resident and beneficiary of any foreign trust, details of that trust need to be mentioned.
Schedule 80G and 80GGA:
- Purpose: These schedules are for reporting donations eligible for tax deductions under specific sections of the Income Tax Act.
- Schedule 80G:
- Donations to certain approved charitable institutions qualify for deductions.
- Depending on the institution, you can claim deductions of 50% or 100% of the donated amount.
- Schedule 80GGA:
- Donations made for scientific research or rural development qualify for deductions under this section.
Schedule AMT/AMTC:
- Purpose: Alternate Minimum Tax (AMT) is a tax levied on certain taxpayers to ensure they pay a minimum amount of tax, even after claiming various deductions and exemptions. If your income falls under the AMT ambit, you need to fill this schedule.
- Details:
- Adjusted total income calculation as per AMT provisions.
- Tax payable under AMT.
- Credit for AMT paid, which can be carried forward for up to 15 years.
Verification:
- Purpose: This is the final and crucial step in the ITR-2 filing process.
- Process:
- You need to sign the ITR-2 form electronically or physically.
- You confirm that the information provided in the return is true and correct to the best of your knowledge and belief.
- You also authorize the Income Tax Department to verify the information provided.
- Options:
- Electronic Verification Code (EVC) through Aadhaar OTP, net banking, or demat account.
- Sending a signed physical copy of ITR-V (Verification) to the Centralized Processing Centre (CPC) in Bengaluru.
Key Points:
- Complete All Applicable Schedules: It is crucial to fill all the relevant schedules accurately to avoid scrutiny or notices from the Income Tax Department.
- Verification Deadline: If you choose to e-Verify, it should be done within 120 days from the date of filing your return. For sending ITR-V physically, the deadline is also 120 days.
- Consequences of Non-Verification: Your return will be considered invalid if not verified within the stipulated time frame.
Filing Your ITR-2 Online: A Step-by-Step Guide
Filing your ITR-2 online is the most convenient and efficient method. Here's a detailed step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
Step 1: Log in to the Income Tax e-Filing Portal
- Visit the official Income Tax Department e-Filing portal: https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal/
- Log in using your user ID (PAN), password, and captcha code.
- If you don't have an account, register first using your PAN.
Step 2: Start Filing Your Return
- On the dashboard, go to "e-File" > "Income Tax Returns" > "File Income Tax Return."
- Select the Assessment Year (AY 2024-25) and choose "Online" as the mode of filing. Click "Continue."

- If you have a previously saved draft, you can continue with it. Otherwise, click "Start New Filing."
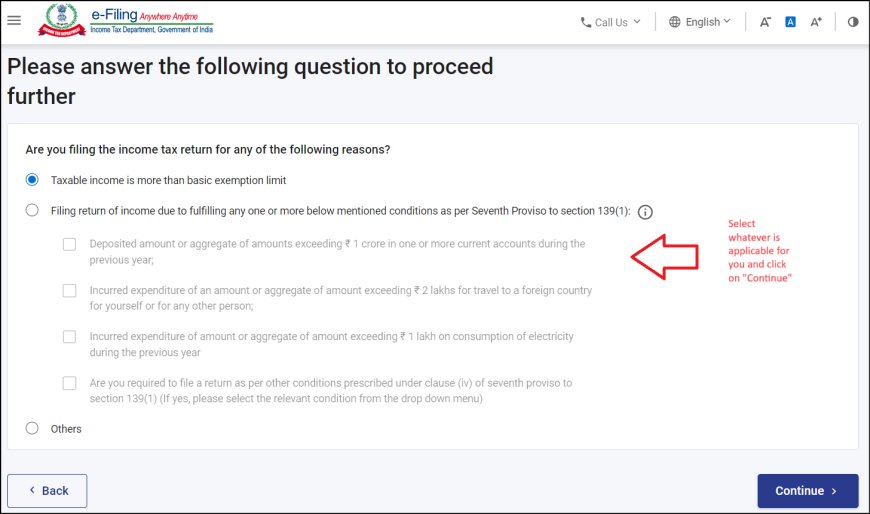
Step 3: Select ITR-2 and Filing Reason
- Select your status (individual, HUF) and click "Continue."

- Choose "ITR-2" from the dropdown menu.

- Select the reason for filing (e.g., income exceeds the basic exemption limit, to claim a refund).
Step 4: Select Schedules
After entering your personal details in Part A of the ITR-2 form, the next crucial step is selecting the applicable schedules and choosing your preferred tax regime. This process can be a bit intricate, so let's break it down:

a) Select Applicable Schedules:
- Purpose: This step involves choosing the schedules relevant to your income sources and deductions.
- Sections:
- General: This schedule is automatically selected as it's mandatory for all taxpayers.
- Income: Select the income schedules that correspond to your income sources (e.g., Schedule S for salary, Schedule HP for house property, Schedule CG for capital gains, Schedule OS for other sources).
- Deductions: Choose the deduction schedules where you have eligible deductions to claim (e.g., Schedule VI-A for deductions under Chapter VI-A, Schedule 80G for donations).
- Tax: These schedules deal with tax calculations and are automatically selected.
- Others: Select any additional schedules applicable to your situation (e.g., Schedule FA for foreign assets).
b) Click "Continue" to Proceed to Schedule Questions:
- After selecting the relevant schedules, click the "Continue" button to move to the next step.
c) Choose New or Old Tax Regime:

- Purpose: The Income Tax Act offers two tax regimes: the new tax regime with lower tax rates but fewer deductions, and the old tax regime with higher tax rates but more deductions.
- Decision: Choose the regime that results in a lower tax liability for you. You can use the "Tax Calculator" on the e-filing portal to compare the tax impact of both regimes.
d) Answer Salary Exemption Questions:

- Purpose: This section is relevant if you have received any exempt income from your salary, such as HRA or LTA.
- Details:
- Answer the questions regarding the exemptions you have availed of.
- Provide details of rent paid, HRA received, travel expenses, etc., to justify your exemption claims.
e) Fill in Deductions:

- Purpose: This step involves entering details of all the deductions you are eligible to claim.
- Schedules:
- Enter the relevant amounts under each deduction section in Schedule VI-A.
- Provide details of your investments, insurance premiums, donations, etc., to support your claims.
f) Click "Continue" to Proceed to Filling Part-A:
- Once you have filled in all the necessary details in the selected schedules, click the "Continue" button to proceed to Part A of the ITR-2 form.
- In Part A, you will review your pre-filled personal information, make any necessary corrections, and move on to the next parts of the form.
Step 5: Fill in Personal Details (Schedule Part A - Gen)
After selecting the applicable schedules and choosing your tax regime, the next step is to fill in your personal details in Schedule Part A - Gen of the ITR-2 form. Here's a detailed guide on how to accurately complete this section:
a) Pre-filled Information:
- Upon entering this section, you'll notice that most of your personal information, such as your name, PAN, Aadhaar, date of birth, and address, is pre-filled from your registered profile on the e-filing portal.
- Review this pre-filled information carefully and make any necessary corrections. If your information has changed (e.g., address), update it in your profile before proceeding.
b) Filing Status:
- Confirm your filing status. Select either "Individual" if you are filing as an individual taxpayer or "HUF" if you are filing on behalf of a Hindu Undivided Family.
c) Residential Status:
- Choose your residential status for the financial year:
- Resident: If you have been in India for 182 days or more during the financial year or 60 days or more in the current year and 365 days or more in the preceding four years.
- Non-Resident (NRI): If you don't meet the criteria for resident status.
- Resident But Not Ordinarily Resident (RNOR): This status is applicable under specific conditions. Consult a tax professional if you think you fall under this category.
d) Bank Account Details:
- Enter your bank account details accurately.
- Ensure the account is in your name.
- Provide the bank's name, account number, type of account (savings or current), and the correct IFSC code.
- Double-check the details to avoid any issues with refunds.
e) Email ID and Mobile Number:
- Provide your valid email address and mobile number.
- The Income Tax Department will use these channels to communicate with you regarding your return, refunds, or any other notifications.
f) Nature of Employment:
- Select the appropriate option from the dropdown menu that reflects your employment status:
- Government
- PSU (Public Sector Undertaking)
- Pensioner
- Others (Private sector, self-employed, etc.)
g) Additional Information (If Applicable):

- Filing Section: If you are filing your return under a specific section of the Income Tax Act, mention the relevant section here.
- Return Filed in Response to Notice: If you're filing this return because you received a notice from the Income Tax Department, check this box.
- Revised Return: If this is a revised return to correct mistakes in a previously filed return, select this option.

Step 6: Fill in Income Details
After filling in your personal details in Part A, the next crucial step in filing ITR-2 is to accurately report your income from various sources. This is done by filling in the relevant schedules in Part B of the form. Let's delve deeper into how to fill in the income details for each schedule:
a) Schedule S: Income from Salaries
- Purpose: To report income earned from your employment.
- Details:
- Basic Salary: Enter your gross salary before any deductions.
- Allowances: Report all allowances received, such as HRA, DA, transport allowance, etc.
- Perquisites: Enter the value of any non-cash benefits provided by your employer, like a company car, accommodation, etc.
- Profit in lieu of Salary: If you received any compensation in lieu of salary, report it here.
- Deductions:
- Standard Deduction: Claim the standard deduction of ₹50,000 (or your actual salary, whichever is lower).
- Entertainment Allowance: Enter the amount of entertainment allowance received (if applicable).
- Professional Tax: Report the professional tax paid by you.
Must Read: How to File Salary Schedule in ITR: Step-by-Step Guide for Indian Taxpayers
b) Schedule HP: Income from House Property
- Purpose: To report income and expenses related to house property.
- Details:
- Gross Annual Value (GAV): Enter the annual rent received or the expected rent if the property is vacant.
- Municipal Taxes: Report the amount of municipal taxes paid on the property.
- Interest on Home Loan: Enter the interest paid on your home loan during the year.
- Standard Deduction: Claim 30% of the net annual value (NAV) as a standard deduction.
- Other Deductions: If you have incurred any other expenses for repairs, maintenance, etc., you can claim them here.
Must Read: How to File Schedule House Property in ITR: Step-by-Step Guide
c) Schedule CG: Capital Gains
- Purpose: To report gains or losses from the sale of capital assets.
- Details:
- Short-term Capital Gains (STCG): Report gains from assets held for 36 months or less (12 months for equity shares/units of equity-oriented funds).
- Long-term Capital Gains (LTCG): Report gains from assets held for more than 36 months (12 months for equity shares/units of equity-oriented funds).
- Exemptions: If you have invested the LTCG in specified assets, you can claim exemptions under relevant sections.
Must Read: How to File Schedule Capital Gains (CG) in ITR: The Complete Guide for Indian Taxpayers
d) Schedule OS: Income from Other Sources
- Purpose: To report income from sources not covered elsewhere.
- Details:
- Interest Income: Report interest earned from savings accounts, FDs, RDs, etc.
- Dividend Income: Enter the dividend income received from your investments.
- Family Pension: Report any family pension received.
- Agricultural Income: If your agricultural income exceeds ₹5,000, report it here.
- Other Income: Include any other miscellaneous income, such as winnings from lotteries, income from freelancing, etc.
e) Other Schedules (112A, 115AD(1)(iii) proviso, VDA, SPI, SI, EI, PTI):
- Purpose: Fill these schedules as per your specific income sources and circumstances.
- Details:
- Refer to the instructions provided in the ITR-2 form or consult a tax professional if you are unsure about any of these schedules.
Also Read: For details on filing individual schedules, check out our articles on Indian Tax Filing.
Step 7: Claim Deductions
After reporting your income in Part B, the next crucial step is to claim deductions in Part C to reduce your taxable income. Schedule VI-A is where you list all the deductions you are eligible to claim under Chapter VI-A of the Income Tax Act. Let's explore this schedule in detail:

a) Section 80C: Deductions for Investments and Expenses
- Maximum Limit: Up to ₹1.5 lakhs
- Eligible Investments/Expenses:
- Life Insurance Premiums: Premiums paid for yourself, your spouse, or your children.
- Equity Linked Saving Schemes (ELSS): Investments in specific mutual funds with a lock-in period of 3 years.
- Public Provident Fund (PPF): Deposits made in this long-term savings scheme.
- National Savings Certificates (NSC): Investments in these government-backed savings certificates.
- Employee Provident Fund (EPF): Contributions made by you or your employer.
- Unit Linked Insurance Plans (ULIPs): Investments in these insurance-cum-investment plans.
- Principal Repayment of Home Loan: Principal amount repaid on your home loan.
- Tuition Fees: Tuition fees paid for the education of your children (maximum two children).
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY): Deposits made in this scheme for the girl child.
- Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS): Deposits made in this scheme for senior citizens.
- National Pension System (NPS): Contributions made towards the NPS.
- Stamp Duty and Registration Charges: For the purchase of a new house property.
b) Section 80D: Deduction for Medical Insurance Premium
- Maximum Limit:
- ₹25,000 for self, spouse, and dependent children.
- Additional ₹25,000 for parents below 60 years or ₹50,000 if parents are senior citizens.
- Eligible Expenses:
- Health insurance premiums paid for yourself, your spouse, dependent children, and parents.
- Preventive health check-up expenses up to ₹5,000.
c) Section 80G: Deductions for Donations
- Deduction Percentage: Varies based on the type of donation and the organization receiving it (50%, 100%, or 100% with a qualifying limit).
- Eligible Donations:
- Donations to the Prime Minister's National Relief Fund.
- Donations to the National Defence Fund.
- Donations to certain approved charitable institutions.
d) Other Important Deductions:
- Section 80E: Deduction for interest paid on education loan.
- Section 80EE: Additional deduction on interest paid on home loan for first-time homebuyers.
- Section 80EEA: Deduction for interest on affordable housing loan.
- Section 80DD: Deduction for medical treatment of specified disabilities.
- Section 80DDB: Deduction for medical treatment of specified diseases for self or dependents.
- Section 80U: Deduction for individuals with disabilities.

Step 8: Verify Tax Calculation and Pay Taxes (if applicable)
After filling in your income details and claiming deductions, the next crucial step in filing your ITR-2 is to verify the tax calculation and pay any taxes due. Here's a detailed guide to help you through this process:

a) Tax Calculation:
- Automatic Calculation: The e-filing portal will automatically calculate your tax liability based on the information you've provided in the previous sections (income, deductions, etc.).
- Tax Computation Details: The portal will display a summary of your tax computation, including:
- Gross Total Income (GTI)
- Total Deductions
- Total Taxable Income (TTI)
- Tax Payable
- Rebate (if eligible)
- Surcharge
- Health & Education Cess
- Total Tax Liability
b) Cross-Verify Tax Calculation:
- Importance: It's crucial to cross-verify the tax calculation done by the portal with your own calculations.
- Check Against Form 26AS: Compare the TDS details in your Form 26AS with those in the ITR-2 form to ensure accuracy.
- Review Deductions: Double-check if all eligible deductions have been claimed and the amounts entered are correct.
- Tax Rates: Verify if the correct tax rates have been applied based on your income and the chosen tax regime.
c) Payment of Taxes (if applicable):
- Tax Due: If the tax calculation shows that you have any tax payable, you need to pay it before filing your return.
- Payment Options: The e-filing portal offers various payment options:
- Net Banking: Pay directly from your bank account.
- Debit Card: Make payment using your debit card.
- Credit Card: Certain banks allow tax payment through credit cards.
- Challan 280: Generate a challan and pay at designated bank branches.
- Payment Details: Enter the details of your payment (BSR code, challan number, date of payment, amount) in the relevant section of the ITR-2 form.
d) After Tax Payment:
- Re-calculate Tax: Once the tax payment is done, re-calculate the tax liability to ensure it's zero or shows a refund due.
- Review: Carefully review all the details once again before moving to the next steps of validation and submission.
Step 9: Validate Your Return

The validation step is a crucial stage in filing your ITR-2 form. It acts as a safety net to catch any errors or inconsistencies you might have inadvertently made while filling out the form. Here's a detailed breakdown of this essential step:
a) Initiate Validation:
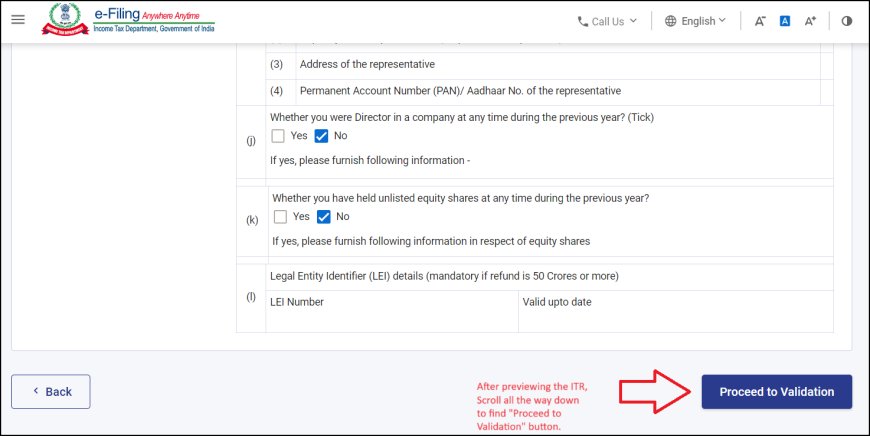
- Locate the "Validate" button: Once you have filled in all the required information in the ITR-2 form, look for a prominent "Validate" button.
- Click the Button: Click on the "Validate" button to initiate the validation process.
b) Validation Process:
- Comprehensive Check: The e-filing portal's validation engine will perform a thorough check of your entire ITR-2 form.
- Data Matching: It will verify if the information provided matches your PAN details, Aadhaar details, Form 16/26AS, and other supporting documents.
- Calculations: It will check if the income and deduction calculations are correct and if the tax liability is calculated accurately.
- Mandatory Fields: It will ensure that all mandatory fields have been filled in.
c) Error Identification:

- Errors Highlighted: If the system finds any errors or inconsistencies, it will highlight them on the screen.
- Error Types:
- Calculation Errors: Incorrect calculations of income, deductions, or tax liability.
- Mismatch with Form 16/26AS: Discrepancies in income or TDS details compared to your Form 16/26AS.
- Missing Information: Incomplete or missing information in mandatory fields.
- Other Errors: Any other inconsistencies in the data provided.
d) Rectify Errors:
- Review Errors: Carefully review each error highlighted by the system.
- Navigate to Relevant Sections: Go back to the relevant sections of the ITR-2 form to rectify the errors.
- Make Corrections: Make the necessary changes in the data entered.
- Re-validate: After making corrections, click the "Validate" button again to ensure all errors have been rectified.
e) Successful Validation:

- Confirmation Message: Once all errors are fixed, the system will display a confirmation message indicating successful validation.
- Proceed to Next Steps: You can then proceed to the next steps of generating and submitting the XML file for e-filing.
Step 10: Proceed to Verification

- Once your return is error-free, click the "Proceed to Verification" button.
- You will see three methods to verify the ITR: e-verify now (recommended), e-verify later or verify via ITR-V. Select whatever suits you.
- Complete the e-Verification process to successfully submit your return.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing ITR-2
Filing your income tax return accurately and on time is essential to comply with tax laws and avoid unnecessary hassles. However, there are several common mistakes that taxpayers often make while filing ITR-2. Let's explore these mistakes and how to avoid them:
1. Ignoring Due Dates:
- Consequence: Missing the deadline for filing your ITR-2 can lead to penalties, interest charges, and even loss of certain benefits like carrying forward losses.
- How to Avoid:
- Mark Your Calendar: Note down the due date for filing ITR-2 (usually July 31st) well in advance.
- Start Early: Begin collecting your documents and filling out the form early to avoid last-minute rush.
- Set Reminders: Use calendar alerts or reminder apps to prompt you about the deadline.
- File Before Deadline: If you anticipate any delays, try to file your return well before the due date.
2. Incorrect Personal Information:
- Consequence: Errors in personal information, such as your name, PAN, Aadhaar, address, or bank details, can lead to processing delays, rejections, or incorrect refunds.
- How to Avoid:
- Verify Details: Double-check all personal information before submitting your return.
- Update PAN/Aadhaar: Ensure your PAN and Aadhaar details are updated and linked on the e-filing portal.
- Bank Account Verification: Verify your bank account details to ensure accurate refunds.
3. Not Reporting All Income Sources:
- Consequence: Failing to report all your income sources, including interest income, rental income, or income from freelance work, can raise red flags with the tax authorities, leading to scrutiny and potential penalties.
- How to Avoid:
- Comprehensive Reporting: Report income from all sources, even if it seems minor.
- Form 26AS: Cross-check your Form 26AS to ensure all your income sources and TDS are correctly reflected.
- Trace Missing Income: If you find discrepancies in your Form 26AS, investigate and report any missing income.
4. Claiming Wrong Deductions:
- Consequence: Claiming deductions you are not eligible for or exceeding the prescribed limits can lead to your return being flagged for scrutiny or even penalties.
- How to Avoid:
- Eligibility Check: Carefully read the eligibility criteria for each deduction before claiming it.
- Documentation: Maintain proper documentation (receipts, investment proofs, etc.) to support your claims.
- Consult a Professional: If you have doubts about any deduction, consult a tax professional.
5. Other Common Mistakes:
- Selecting the Wrong ITR Form: Choose the correct ITR form based on your income sources and residential status.
- Not Verifying Your Return: E-verification or sending ITR-V is essential to make your return valid.
- Ignoring Communication from the IT Department: Respond promptly to any notices or queries from the tax authorities.
Benefits of Filing ITR-2 on Time
Timely filing of your Income Tax Return (ITR-2) is not just a legal obligation; it comes with a multitude of financial and non-financial benefits. Here's an expanded look at the advantages of filing your ITR-2 before the due date:
1. Avoid Penalties and Interest:
- Late Filing Penalty: Filing your ITR-2 after the due date can attract a late filing fee under Section 234F of the Income Tax Act. The penalty can range from ₹1,000 to ₹5,000, depending on the delay.
- Interest on Tax Due: If you have any tax due, failing to file on time can lead to interest charges on the outstanding amount.
2. Easy Loan and Credit Card Approval:
- Proof of Income: Banks and financial institutions often require your ITR as proof of income when you apply for loans or credit cards.
- Higher Loan Amount: A timely filed ITR with a good income record can help you secure a higher loan amount or better credit card terms.
- Faster Processing: Loan applications are processed faster when you have a recent ITR.
3. Claim Tax Refunds:
- Excess TDS: If your employer or other deductors have deducted more TDS than your actual tax liability, you can claim a refund by filing your ITR-2.
- Timely Refund: Filing your return on time ensures that you receive your refund sooner.
4. Carry Forward Losses:
- Business Losses: If you have incurred losses from your house property or capital gains, you can carry them forward for up to 8 assessment years to set them off against future income of the same head.
- Tax Savings: This can help you reduce your tax liability in future years.
5. Visa Application:
- Proof of Financial Stability: Many countries require a copy of your ITR for visa applications to assess your financial stability.
6. Avoiding Scrutiny:
- Reduced Risk: Filing your ITR-2 on time reduces the chances of your return being selected for scrutiny by the Income Tax Department.
7. Peace of Mind:
- Compliance: Filing your return within the deadline ensures that you are compliant with tax laws.
- Stress-free: You avoid the stress and anxiety associated with last-minute filings and potential penalties.
8. Building a Financial Track Record:
- Financial Discipline: Consistently filing your ITR on time demonstrates financial discipline and responsibility.
- Future Benefits: A good tax filing history can be beneficial for various financial transactions and opportunities.
9. Contributing to Nation Building:
- Tax Revenue: Your taxes contribute to the development and welfare of the country.
Conclusion: Master ITR-2 Filing with Confidence
Navigating the intricacies of income tax filing in India can often seem overwhelming, especially with the various forms and schedules involved. However, as this comprehensive guide demonstrates, filing your ITR-2 form doesn't have to be a daunting task. By breaking down the process into manageable steps, we've aimed to demystify the filing procedure and equip you with the knowledge and tools needed for a successful filing.
Key Takeaways:
- Preparation is Key: Gathering all your documents beforehand streamlines the process and minimizes errors.
- Understanding the Form: Familiarize yourself with the different sections and schedules to ensure accurate reporting of income and deductions.
- Choose Your Regime Wisely: Carefully consider the old and new tax regimes to determine which one benefits you the most.
- Double-Check: Always review your entries thoroughly before submitting your return to avoid mistakes and potential scrutiny.
- Seek Help: If you encounter any difficulties or have complex financial situations, don't hesitate to seek professional guidance from a chartered accountant or tax expert.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can confidently file your ITR-2 form on time, ensuring compliance with tax laws and minimizing your tax liability. Remember, accurate and timely filing is not only a legal requirement but also a responsible financial practice that can save you from penalties and contribute to the nation's development.
Additional Tips:
- Stay Updated: Tax laws and regulations are subject to change. Keep yourself updated with the latest information from the Income Tax Department's official website or reliable sources.
- Use Online Resources: The Income Tax Department provides online tools and resources like the "Tax Calculator" and FAQs to assist taxpayers.
- E-Filing is Convenient: Embrace the convenience of e-filing your ITR-2 online through the official portal. It's faster, easier, and more efficient than the traditional paper-based filing.
Filing your ITR-2 is a significant financial responsibility, but with the right information and approach, it can be a straightforward process. By understanding the requirements, utilizing the resources available, and following the steps outlined in this guide, you can successfully file your return and contribute to a hassle-free tax season.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as professional tax or legal advice. Tax laws and regulations are subject to change, and individual circumstances may vary. While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the information contained in this article. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk. We recommend consulting with a qualified tax professional or chartered accountant for personalized advice regarding your specific tax situation.
What's Your Reaction?
































































































































